Have you ever wondered how an image can be recreated by evolutionary principles? Genetic algorithms (GA) provide a fascinating way to approach this challenge. They simulate the process of natural selection by evolving a population of potential solutions over successive generations.
In this project, I revisited an open-source contribution I made years ago, where I attempted to replicate user-uploaded images using a genetic algorithm. Although the original pull request was not accepted due to some unnoticed broken code, my fascination with the concept never faded. Inspired to refine it, I rebuilt and enhanced the implementation. Here’s the full story of how it works.
What is a Genetic Algorithm?
A genetic algorithm is an optimization technique inspired by natural evolution. It works by:
- Initialization: Generating an initial population of potential solutions.
- Evaluate Fitness: Measure how closely each solution resembles the target.
- Selection: Choose the best candidates to pass their traits to the next generation.
- Crossover: Combining pairs of solutions to produce offspring.
- Mutation: Randomly altering some solutions to introduce variation.
- Iteration: Repeating the process over multiple generations until a solution emerges.
In this project, the algorithm attempts to match an uploaded image by evolving randomly generated shapes on a canvas.
Project Overview
In this project, users can upload an image, and the algorithm will attempt to replicate it by evolving random patterns. Each generation produces better approximations of the original image by evaluating and evolving previous solutions.
Setting Up the HTML
We’ll start with a simple HTML structure that includes an upload button, two canvases (for the target and evolving images), and a button to start the algorithm.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Genetic Algorithm - Image Matching</title>
<style>
body {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
margin: 0;
}
.container {
display: flex;
}
.container div {
margin: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Upload an Image for Matching</h1>
<input type="file" id="imageUpload" accept="image/*" />
<br/><br/>
<div class="container">
<div>
<h2>Uploaded Image:</h2>
<canvas id="uploadedCanvas" width="300" height="300"></canvas>
</div>
<div>
<h2>Genetic Algorithm Output:</h2>
<canvas id="outputCanvas" width="300" height="300"></canvas>
<p>Current match: <span id="matchPercentage"></span>%</p>
<p>Generation: <span id="generationCount"></span></p>
<br/>
<button id="startGeneticAlgorithm">Start Genetic Algorithm</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const uploadedCanvas = document.getElementById("uploadedCanvas");
const outputCanvas = document.getElementById("outputCanvas");
const ctxUploaded = uploadedCanvas.getContext("2d");
const ctxOutput = outputCanvas.getContext("2d");
const matchSpan = document.getElementById("matchPercentage");
const genSpan = document.getElementById("generationCount");
let targetData = null;
const imageUpload = document.getElementById("imageUpload");
imageUpload.addEventListener("change", handleImageUpload);
function handleImageUpload(event) {
const file = event.target.files[0];
if (file) {
const targetImage = new Image();
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = function(e) {
targetImage.src = e.target.result;
};
targetImage.onload = function() {
ctxUploaded.clearRect(0, 0, uploadedCanvas.width, uploadedCanvas.height);
ctxUploaded.drawImage(targetImage, 0, 0, uploadedCanvas.width, uploadedCanvas.height);
targetData = getImageData(targetImage);
};
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
}
}
function getImageData(image) {
ctxOutput.clearRect(0, 0, outputCanvas.width, outputCanvas.height);
ctxOutput.drawImage(image, 0, 0, outputCanvas.width, outputCanvas.height);
return ctxOutput.getImageData(0, 0, outputCanvas.width, outputCanvas.height);
}
const startButton = document.getElementById("startGeneticAlgorithm");
startButton.addEventListener("click", startGeneticAlgorithm);
function startGeneticAlgorithm() {
if (!targetData) {
alert("Please upload an image first.");
return;
}
const populationSize = 50;
let population = new ImageSamplePopulation(targetData, populationSize);
population.populate();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Implementing the Genetic Algorithm
The following code defines two classes, ImageSample and ImageSamplePopulation, which handle the creation, mutation, and evolution of images.
class ImageSample {
constructor(config) {
this.mutationRate = config.mutationRate;
this.shapeRate = config.shapeRate;
this.target = config.target
this.width = config.width;
this.height = config.height;
if (config.image) {
this.image = config.image;
} else {
this.randomizeImage();
}
}
randomizeImage() {
let baseImageLayer = new ImageData(this.width, this.height);
if (this.image) {
baseImageLayer = this.image;
}
ctxOutput.putImageData(baseImageLayer, 0, 0);
const color = this.getRandomColor();
if (Math.random() < this.shapeRate) {
const x = this.getRandomInt(0, this.width);
const y = this.getRandomInt(0, this.height);
const radius = this.getRandomFloat(1, Math.min(this.width / 2, this.height / 2));
this.drawCircle(ctxOutput, color, x, y, radius);
} else {
let coordinates = [
this.getRandomInt(0, this.width),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.height),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.width),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.height),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.width),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.height),
];
this.drawShape(ctxOutput, color, coordinates);
}
this.image = ctxOutput.getImageData(0, 0, this.width, this.height);
this.fitness = this.computeFitness(this.target);
}
getRandomColor() {
var letters = "0123456789ABCDEF";
var color = "#";
for (var i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
color += letters[Math.floor(Math.random() * 16)];
}
return color;
}
getRandomInt(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min)) + min;
}
getRandomFloat(min, max) {
return Math.random() * (max - min) + min;
}
drawLine(ctx, color, x1, y1, x2, y2, width) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(x1, y1);
ctx.lineTo(x2, y2);
ctx.strokeStyle = color;
ctx.lineWidth = width;
ctx.stroke();
}
drawCircle(ctx, color, x, y, radius) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(x, y, radius, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.fill();
}
drawEllipse(ctx, color, x, y, radiusX, radiusY) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.ellipse(x, y, radiusX, radiusY, 0, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.fill();
}
drawShape(ctx, color, coords) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(coords[0], coords[1]);
for (let i = 2; i < coords.length; i += 2) {
ctx.lineTo(coords[i], coords[i + 1]);
}
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.fill();
}
mutate() {
const mutationResistance = 0.5;
if (this.mutationRate < mutationResistance) return;
this.randomizeImage();
}
crossover(partner) {
let crossoverRate = Math.floor(Math.random() * partner.image.data.length);
crossoverRate = crossoverRate > 0 ? crossoverRate : 0.5;
const parentsMutationRate = (this.mutationRate + partner.mutationRate) / 2;
const parentsShapeRate = (this.shapeRate + partner.shapeRate) / 2;
let offspringImage = this.image;
const parentImageData1 = this.image.data;
const parentImageData2 = partner.image.data;
for (var i = 0; i < parentImageData1.length; i += 4) {
offspringImage.data[i] = parentImageData1[i] * crossoverRate + parentImageData2[i] * (1 - crossoverRate); // red
offspringImage.data[i + 1] = parentImageData1[i + 1] * crossoverRate + parentImageData2[i + 1] * (1 - crossoverRate); // green
offspringImage.data[i + 2] = parentImageData1[i + 2] * crossoverRate + parentImageData2[i + 2] * (1 - crossoverRate); // blue
}
const offspring = {
mutationRate: (Math.random() + parentsMutationRate) / 2,
shapeRate: (Math.random() + parentsShapeRate) / 2,
target: this.target,
width: this.width,
height: this.height,
image: offspringImage
};
return new ImageSample(offspring);
}
computeFitness() {
this.fitness = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < this.target.data.length; i += 4) {
this.fitness += Math.sqrt(
Math.pow(this.target.data[i] - this.image.data[i], 2)
+ Math.pow(this.target.data[i + 1] - this.image.data[i + 1], 2)
+ Math.pow(this.target.data[i + 2] - this.image.data[i + 2], 2)
);
}
}
hasAchievedTarget() {
return this.image == this.target
}
}
class ImageSamplePopulation {
constructor(target, populationSize) {
this.imageSamples = [];
this.oldImageSamples = [];
const { width, height } = target;
this.target = target;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.generationNo = 0;
while (populationSize--) {
this.imageSamples.push(new ImageSample({
mutationRate: Math.random(),
shapeRate: Math.random(),
target: this.target,
width: this.width,
height: this.height
}));
}
this.bestImageSample = this.imageSamples[0];
this.elitismCount = Math.ceil(this.imageSamples.length * 0.5);
}
sortFitness(a, b) {
return a.fitness - b.fitness;
}
showGeneration() {
const maxDiff = this.width * this.height * 3 * 255;
genSpan.textContent = this.generationNo;
matchSpan.textContent = (100 * (1 - this.bestImageSample.fitness / maxDiff)).toFixed(2);
ctxOutput.putImageData(this.bestImageSample.image, 0, 0);
}
populate() {
this.imageSamples.sort(this.sortFitness);
this.showGeneration();
this.oldImageSamples = this.imageSamples;
let isPerfectGeneration = false;
const offspringCount = this.imageSamples.length - this.elitismCount;
let offsprings = [];
for (let i = 0; i < offspringCount; i++) {
const bestParent = this.imageSamples[0];
const randomParent = this.imageSamples[1];
const offspring = bestParent.crossover(randomParent);
offsprings.push(offspring);
}
this.imageSamples.splice(this.imageSamples.length - offsprings.length, offsprings.length, ...offsprings);
this.imageSamples.forEach(sample => {
sample.mutate();
sample.computeFitness();
if (sample.hasAchievedTarget()) {
isPerfectGeneration = true;
}
})
if (isPerfectGeneration) {
this.imageSamples.sort(this.sortFitness);
this.showGeneration();
} else {
this.generationNo++;
const self = this;
setTimeout(function() {
const oldImageSamplesTargetCount = Math.ceil(self.elitismCount / 2);
const newImageSamplesTargetCount = Math.ceil(self.elitismCount / 2);
const bestImageSamples = [
...self.findBestImageSamples(self.oldImageSamples, oldImageSamplesTargetCount),
...self.findBestImageSamples(self.imageSamples, newImageSamplesTargetCount)
];
bestImageSamples.sort(self.sortFitness);
self.bestImageSample = bestImageSamples[0];
for (let i = bestImageSamples.length; i < self.imageSamples.length; i++) {
self.imageSamples[i].image = bestImageSamples[i % bestImageSamples.length].image;
self.imageSamples[i].fitness = bestImageSamples[i % bestImageSamples.length].fitness;
}
self.populate();
}, 0);
}
}
findBestImageSamples(arr, len) {
if (arr.length < len) len = arr.length - 1;
return [...arr].sort((a, b) => a.fitness - b.fitness).slice(0, len)
}
}Class: ImageSample
Represents an individual image sample in the population, including methods for mutation, crossover, and fitness calculation. Each ImageSample is an attempt to approximate the target image.
Constructor: constructor(config)
Initializes the ImageSample instance with given configuration values.
Parameters:
config(Object): Configuration object with the following properties:mutationRate(number): Probability of mutation during evolution.shapeRate(number): Probability of adding a shape (circle or polygon).target(ImageData): Target image data to approximate.width(number): Width of the image.height(number): Height of the image.image(ImageData, optional): Initial image data (optional).
Methods:
randomizeImage()
- Randomizes the
ImageSampleby drawing either a circle or polygon with random properties.
getRandomColor()
- Generates a random hexadecimal color string.
getRandomInt(min, max)
- Returns a random integer between
min(inclusive) andmax(exclusive).
getRandomFloat(min, max)
- Returns a random floating-point number between
minandmax.
drawLine(ctx, color, x1, y1, x2, y2, width)
- Draws a line on the canvas.
drawCircle(ctx, color, x, y, radius)
- Draws a filled circle on the canvas.
drawEllipse(ctx, color, x, y, radiusX, radiusY)
- Draws a filled ellipse on the canvas.
drawShape(ctx, color, coords)
- Draws a polygon with the given coordinates.
mutate()
- Randomizes the image based on the mutation rate, introducing variation.
crossover(partner)
- Combines the image data of two
ImageSampleinstances to create an offspring.
computeFitness()
- Calculates the fitness of the current image by comparing it to the target image.
hasAchievedTarget()
- Checks if the current image matches the target image exactly.
Class: ImageSamplePopulation
Represents a population of ImageSample instances, controlling the evolution process over multiple generations using genetic algorithm techniques like elitism and crossover.
Constructor: constructor(target, populationSize)
Initializes the ImageSamplePopulation with a target image and a population size.
Parameters:
target(ImageData): The target image data to evolve toward.populationSize(number): Number ofImageSampleinstances in the population.
Methods:
sortFitness(a, b)
- Sorts two
ImageSampleinstances by fitness.
showGeneration()
- Displays the best
ImageSamplein the current generation and updates the fitness percentage.
populate()
- Advances the population by one generation, performing crossover, mutation, and elitism.
findBestImageSamples(arr, len)
- Finds the
lenbestImageSampleinstances from an array based on fitness.
Complete Project Code
Below is the complete code for the project, ready for you to explore and experiment with:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Genetic Algorithm - Image Matching</title>
<style>
body {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
margin: 0;
}
.container {
display: flex;
}
.container div {
margin: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Upload an Image for Matching</h1>
<input type="file" id="imageUpload" accept="image/*" />
<br/><br/>
<div class="container">
<div>
<h2>Uploaded Image:</h2>
<canvas id="uploadedCanvas" width="300" height="300"></canvas>
</div>
<div>
<h2>Genetic Algorithm Output:</h2>
<canvas id="outputCanvas" width="300" height="300"></canvas>
<p>Current match: <span id="matchPercentage"></span>%</p>
<p>Generation: <span id="generationCount"></span></p>
<br/>
<button id="startGeneticAlgorithm">Start Genetic Algorithm</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
class ImageSample {
constructor(config) {
this.mutationRate = config.mutationRate;
this.shapeRate = config.shapeRate;
this.target = config.target
this.width = config.width;
this.height = config.height;
if (config.image) {
this.image = config.image;
} else {
this.randomizeImage();
}
}
randomizeImage() {
let baseImageLayer = new ImageData(this.width, this.height);
if (this.image) {
baseImageLayer = this.image;
}
ctxOutput.putImageData(baseImageLayer, 0, 0);
const color = this.getRandomColor();
if (Math.random() < this.shapeRate) {
const x = this.getRandomInt(0, this.width);
const y = this.getRandomInt(0, this.height);
const radius = this.getRandomFloat(1, Math.min(this.width / 2, this.height / 2));
this.drawCircle(ctxOutput, color, x, y, radius);
} else {
let coordinates = [
this.getRandomInt(0, this.width),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.height),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.width),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.height),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.width),
this.getRandomInt(0, this.height),
];
this.drawShape(ctxOutput, color, coordinates);
}
this.image = ctxOutput.getImageData(0, 0, this.width, this.height);
this.fitness = this.computeFitness(this.target);
}
getRandomColor() {
var letters = "0123456789ABCDEF";
var color = "#";
for (var i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
color += letters[Math.floor(Math.random() * 16)];
}
return color;
}
getRandomInt(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min)) + min;
}
getRandomFloat(min, max) {
return Math.random() * (max - min) + min;
}
drawLine(ctx, color, x1, y1, x2, y2, width) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(x1, y1);
ctx.lineTo(x2, y2);
ctx.strokeStyle = color;
ctx.lineWidth = width;
ctx.stroke();
}
drawCircle(ctx, color, x, y, radius) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(x, y, radius, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.fill();
}
drawEllipse(ctx, color, x, y, radiusX, radiusY) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.ellipse(x, y, radiusX, radiusY, 0, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.fill();
}
drawShape(ctx, color, coords) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(coords[0], coords[1]);
for (let i = 2; i < coords.length; i += 2) {
ctx.lineTo(coords[i], coords[i + 1]);
}
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.fill();
}
mutate() {
const mutationResistance = 0.5;
if (this.mutationRate < mutationResistance) return;
this.randomizeImage();
}
crossover(partner) {
let crossoverRate = Math.floor(Math.random() * partner.image.data.length);
crossoverRate = crossoverRate > 0 ? crossoverRate : 0.5;
const parentsMutationRate = (this.mutationRate + partner.mutationRate) / 2;
const parentsShapeRate = (this.shapeRate + partner.shapeRate) / 2;
let offspringImage = this.image;
const parentImageData1 = this.image.data;
const parentImageData2 = partner.image.data;
for (var i = 0; i < parentImageData1.length; i += 4) {
offspringImage.data[i] = parentImageData1[i] * crossoverRate + parentImageData2[i] * (1 - crossoverRate); // red
offspringImage.data[i + 1] = parentImageData1[i + 1] * crossoverRate + parentImageData2[i + 1] * (1 - crossoverRate); // green
offspringImage.data[i + 2] = parentImageData1[i + 2] * crossoverRate + parentImageData2[i + 2] * (1 - crossoverRate); // blue
}
const offspring = {
mutationRate: (Math.random() + parentsMutationRate) / 2,
shapeRate: (Math.random() + parentsShapeRate) / 2,
target: this.target,
width: this.width,
height: this.height,
image: offspringImage
};
return new ImageSample(offspring);
}
computeFitness() {
this.fitness = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < this.target.data.length; i += 4) {
this.fitness += Math.sqrt(
Math.pow(this.target.data[i] - this.image.data[i], 2)
+ Math.pow(this.target.data[i + 1] - this.image.data[i + 1], 2)
+ Math.pow(this.target.data[i + 2] - this.image.data[i + 2], 2)
);
}
}
hasAchievedTarget() {
return this.image == this.target
}
}
class ImageSamplePopulation {
constructor(target, populationSize) {
this.imageSamples = [];
this.oldImageSamples = [];
const { width, height } = target;
this.target = target;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.generationNo = 0;
while (populationSize--) {
this.imageSamples.push(new ImageSample({
mutationRate: Math.random(),
shapeRate: Math.random(),
target: this.target,
width: this.width,
height: this.height
}));
}
this.bestImageSample = this.imageSamples[0];
this.elitismCount = Math.ceil(this.imageSamples.length * 0.5);
}
sortFitness(a, b) {
return a.fitness - b.fitness;
}
showGeneration() {
const maxDiff = this.width * this.height * 3 * 255;
genSpan.textContent = this.generationNo;
matchSpan.textContent = (100 * (1 - this.bestImageSample.fitness / maxDiff)).toFixed(2);
ctxOutput.putImageData(this.bestImageSample.image, 0, 0);
}
populate() {
this.imageSamples.sort(this.sortFitness);
this.showGeneration();
this.oldImageSamples = this.imageSamples;
let isPerfectGeneration = false;
const offspringCount = this.imageSamples.length - this.elitismCount;
let offsprings = [];
for (let i = 0; i < offspringCount; i++) {
const bestParent = this.imageSamples[0];
const randomParent = this.imageSamples[1];
const offspring = bestParent.crossover(randomParent);
offsprings.push(offspring);
}
this.imageSamples.splice(this.imageSamples.length - offsprings.length, offsprings.length, ...offsprings);
this.imageSamples.forEach(sample => {
sample.mutate();
sample.computeFitness();
if (sample.hasAchievedTarget()) {
isPerfectGeneration = true;
}
})
if (isPerfectGeneration) {
this.imageSamples.sort(this.sortFitness);
this.showGeneration();
} else {
this.generationNo++;
const self = this;
setTimeout(function() {
const oldImageSamplesTargetCount = Math.ceil(self.elitismCount / 2);
const newImageSamplesTargetCount = Math.ceil(self.elitismCount / 2);
const bestImageSamples = [
...self.findBestImageSamples(self.oldImageSamples, oldImageSamplesTargetCount),
...self.findBestImageSamples(self.imageSamples, newImageSamplesTargetCount)
];
bestImageSamples.sort(self.sortFitness);
self.bestImageSample = bestImageSamples[0];
for (let i = bestImageSamples.length; i < self.imageSamples.length; i++) {
self.imageSamples[i].image = bestImageSamples[i % bestImageSamples.length].image;
self.imageSamples[i].fitness = bestImageSamples[i % bestImageSamples.length].fitness;
}
self.populate();
}, 0);
}
}
findBestImageSamples(arr, len) {
if (arr.length < len) len = arr.length - 1;
return [...arr].sort((a, b) => a.fitness - b.fitness).slice(0, len)
}
}
const uploadedCanvas = document.getElementById("uploadedCanvas");
const outputCanvas = document.getElementById("outputCanvas");
const ctxUploaded = uploadedCanvas.getContext("2d");
const ctxOutput = outputCanvas.getContext("2d");
const matchSpan = document.getElementById("matchPercentage");
const genSpan = document.getElementById("generationCount");
let targetData = null;
const imageUpload = document.getElementById("imageUpload");
imageUpload.addEventListener("change", handleImageUpload);
function handleImageUpload(event) {
const file = event.target.files[0];
if (file) {
const targetImage = new Image();
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = function(e) {
targetImage.src = e.target.result;
};
targetImage.onload = function() {
ctxUploaded.clearRect(0, 0, uploadedCanvas.width, uploadedCanvas.height);
ctxUploaded.drawImage(targetImage, 0, 0, uploadedCanvas.width, uploadedCanvas.height);
targetData = getImageData(targetImage);
};
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
}
}
function getImageData(image) {
ctxOutput.clearRect(0, 0, outputCanvas.width, outputCanvas.height);
ctxOutput.drawImage(image, 0, 0, outputCanvas.width, outputCanvas.height);
return ctxOutput.getImageData(0, 0, outputCanvas.width, outputCanvas.height);
}
const startButton = document.getElementById("startGeneticAlgorithm");
startButton.addEventListener("click", startGeneticAlgorithm);
function startGeneticAlgorithm() {
if (!targetData) {
alert("Please upload an image first.");
return;
}
const populationSize = 50;
let population = new ImageSamplePopulation(targetData, populationSize);
population.populate();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Recommendation on How to Run the Code
It’s recommended to serve the HTML file using Express.js. Follow the step-by-step guide below to set up an Express.js environment:
Step 1: Install Node.js and npm
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime that allows you to run JavaScript code on the server side. It comes with npm (Node Package Manager), which helps you install and manage packages.
Installation Steps:
- Download and install Node.js from the official website.
- To verify the installation, open your terminal and run:
node -v
npm -vThis should display the installed versions of Node.js and npm.
Step 2: Create a New Project Directory
Open your terminal and create a new directory for the project. Navigate into that directory:
mkdir ga-image-project
cd ga-image-projectAlternatively, you can create a new directory using the file explorer and then open the terminal in that location.
Step 3: Initialize a New Node.js Project
Run the following command to create a package.json file, which will manage your project dependencies:
npm init -yThe -y flag automatically answers "yes" to all prompts, creating a default package.json file.
Step 4: Installing the Dependencies
To install the dependencies, run:
npm install expressStep 5: Setting Up an Express.js Endpoint
Setup a simple Express.js endpoint to serve the HTML file using the following code:
// server.js
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
// Serve static files (images, CSS, etc.) from the "public" directory
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')));
// Handle the route for the homepage, serving the HTML
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'index.html'));
});
// Start the server on port 3000
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on http://localhost:3000');
});Step 6: Start the Server
You may start the server using the following command:
node server.jsOnce, running you should be able to access the page on http://localhost:3000.

Step 7: Generate an Image
Upload your image and watch the algorithm generate an image.
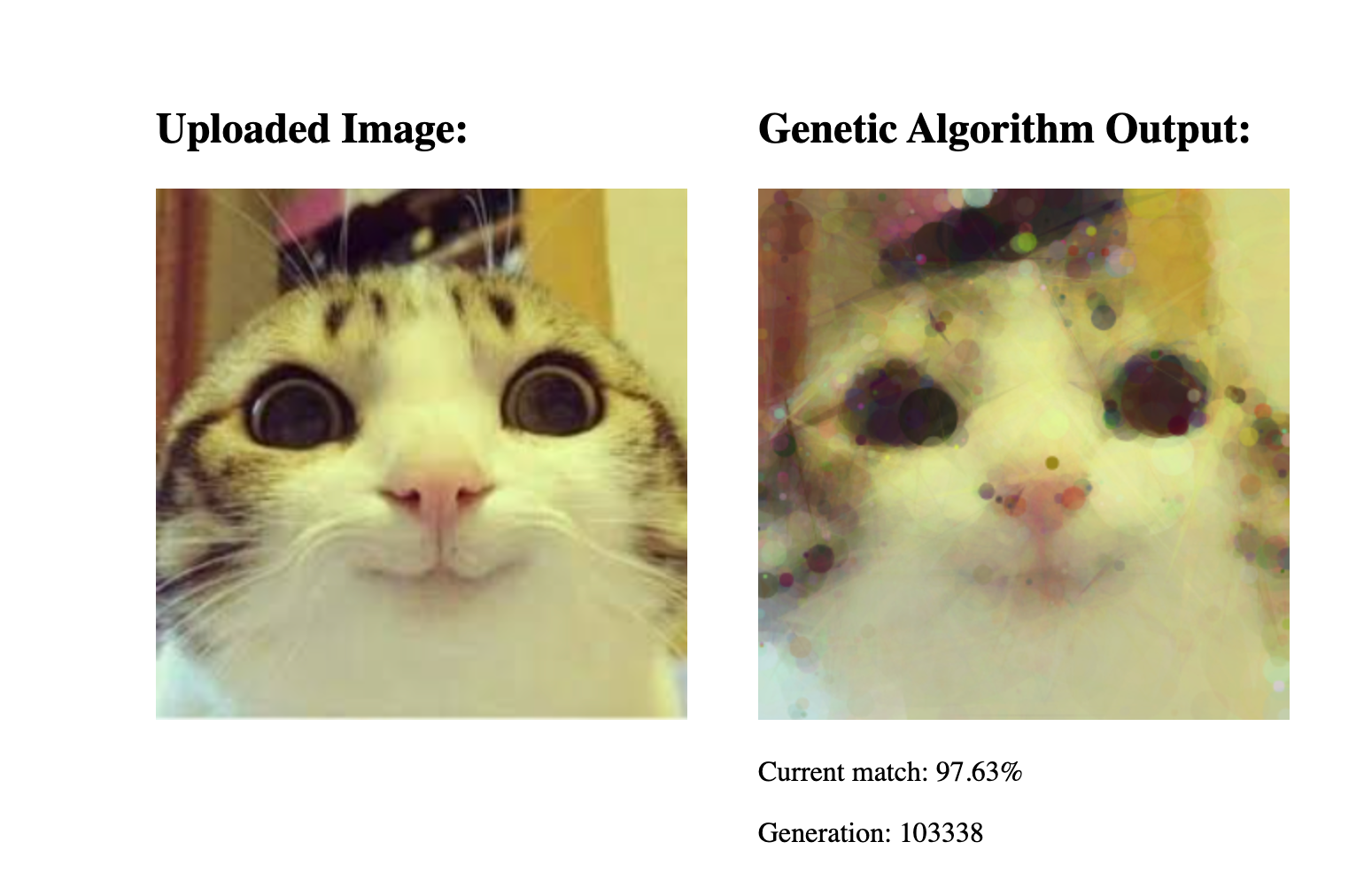
Conclusion
In this exploration of genetic algorithms through image evolution, we’ve seen how simple principles like mutation, crossover, and selection can drive a population of images toward an ideal target. However, this implementation is far from perfect. While it demonstrates the core concepts effectively, it takes time to converge, and the resulting images often come close to the target but rarely achieve exact replication.
This leaves room for improvement — and that’s where the real challenge lies. I encourage you, the reader, to dive deeper into this code, experiment, and find ways to enhance its efficiency and accuracy. Can you make it converge faster? Can you fine-tune the mutation and crossover mechanisms for better results? The beauty of algorithms like this lies in their flexibility, and your innovations could push it to new heights.
Happy coding, and may your evolutionary journey be as rewarding as the process itself!


Comments
Post a Comment